Agentic AI: The Future of Autonomous Intelligence
In the evolving world of artificial intelligence, a new paradigm is gaining momentum—agentic AI. While traditional AI models focus on pattern recognition, prediction, or classification, agentic AI introduces something deeper: autonomous, goal-driven behavior that mimics human-like agency.
As we move toward smarter, more independent machines, understanding what agentic AI is, how it works, and why it matters becomes essential. In this blog post, we’ll explore the concept of agentic AI in depth, look at how it differs from conventional AI, review real-world use cases, and examine the ethical and technical challenges it presents.
What is Agentic AI?
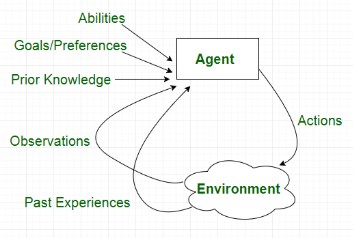
Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to operate with agency—meaning they can set goals, make decisions, take actions, and learn from their outcomes autonomously. These systems are not just tools; they act more like digital “agents” capable of navigating environments and making intelligent choices.
Unlike traditional AI systems that simply respond to input based on pre-trained data, agentic AI can initiate actions without direct human prompts. It understands its environment, reasons about different scenarios, plans steps to reach objectives, and adapts based on results.
In simple terms, agentic AI is about creating systems that “do things” for themselves, not just “process things” for us.
How Agentic AI Works
At the heart of agentic AI is an architecture that supports perception, reasoning, decision-making, and learning. Here are the key components:
-
Perception: The system gathers input from the environment using sensors or APIs (e.g., camera data, user queries, web inputs).
-
Belief System: It builds an internal model of the world, representing what it knows or assumes about the current situation.
-
Goal Setting: It can be given objectives or generate its own based on internal criteria or external context.
-
Planning and Action: The agentic AI system plans a sequence of actions to achieve a goal and executes them.
-
Feedback Loop: It evaluates outcomes and adjusts its strategy, improving future performance.
This dynamic cycle enables agentic AI to go beyond task execution into the realm of intelligent agency.
Agentic AI vs Traditional AI
It’s important to distinguish agentic AI from conventional AI systems. Here’s how they differ:
| Feature | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Low | High |
| Goal Setting | Human-defined | Self-initiated or adaptive |
| Learning Scope | Task-specific | Generalized, cross-domain |
| Interaction Style | Reactive | Proactive |
| Examples | Image classifiers, chatbots | Autonomous drones, digital personal assistants |
While a traditional AI might tell you the weather when asked, agentic AI could reschedule your meeting and notify others if it predicts a storm will interfere with your travel.
Applications of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is already beginning to shape the future of automation, user interaction, and decision-making across various industries.
1. Digital Personal Assistants
Next-gen virtual assistants powered by agentic AI can manage schedules, make bookings, optimize your time, and adjust priorities without constant user input.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Cars using agentic AI can not only drive themselves but also plan fuel stops, reroute based on traffic, or schedule maintenance—all without driver involvement.
3. Healthcare AI
In medicine, agentic AI could monitor a patient’s health metrics in real time, detect anomalies, schedule appointments, and alert emergency services if necessary.
4. Finance and Trading
Autonomous agents in finance can analyze markets, make trading decisions, and rebalance portfolios based on changing economic indicators—learning and adapting without direct instruction.
5. Smart Manufacturing
Agentic AI systems can coordinate production lines, manage supply chains, and troubleshoot faults proactively, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
These applications showcase how agentic AI goes beyond execution—it initiates, decides, and learns.
The Promise of Agentic AI
The real power of agentic AI lies in its ability to reduce the cognitive load on humans. As our lives and industries become more complex, the need for intelligent agents that can handle tasks on our behalf will only grow.
Key benefits of agentic AI include:
-
Increased Productivity: Automating not just tasks, but decision-making processes.
-
Better User Experience: Systems that understand context and adapt accordingly.
-
Faster Innovation: AI that explores new strategies and solutions on its own.
-
Scalability: One agent can handle complex workflows that would require multiple traditional AI systems.
With the rise of agentic AI, we’re looking at a future where machines aren’t just tools—they’re teammates.
Challenges and Concerns Around Agentic AI
Despite its potential, agentic AI brings a range of ethical, technical, and social challenges:
1. Control and Oversight
If an AI system can act independently, how do we ensure it doesn’t pursue harmful goals or act against human interests?
2. Transparency
Agentic systems often involve complex decision-making. Making these processes explainable and auditable is essential.
3. Bias and Fairness
Agentic AI can inherit or even amplify biases if not carefully designed and monitored.
4. Security
A self-directed AI system can be a bigger target for adversarial attacks, especially if it controls critical infrastructure.
5. Responsibility and Accountability
If an agentic AI makes a mistake or causes harm, who is responsible—the developer, the user, or the AI itself?
Solving these problems will require collaboration between technologists, ethicists, policy makers, and the broader public.
The Future of Agentic AI
The future of agentic AI is incredibly exciting. We’re already seeing the groundwork being laid in projects like autonomous agents from OpenAI, Auto-GPT, and autonomous robotics research.
In the next 5–10 years, we can expect:
-
Emotionally Intelligent Agents: Capable of understanding and responding to human emotions.
-
Multi-Agent Collaboration: Teams of AI agents working together to achieve complex goals.
-
Personalized Agentic AI: Tailored agents that deeply understand individual users and evolve over time.
-
Ethical Governance Frameworks: To manage risks and ensure responsible use of agentic AI.
As technology matures, agentic AI could be one of the defining innovations of the 21st century.
Conclusion
Agentic AI represents a major leap forward in artificial intelligence—moving us from passive tools to active collaborators. By designing AI systems with true agency, we enable machines to understand goals, take initiative, and adapt in complex environments.
Whether it’s managing your daily life, optimizing logistics, or powering autonomous systems, agentic AI offers the intelligence and independence needed to meet the demands of the future.
As we continue to develop this technology, it’s vital that we do so thoughtfully, ensuring that agentic AI is transparent, aligned with human values, and beneficial to all.







Leave a Comment