The Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Inconel Forging for Your Needs
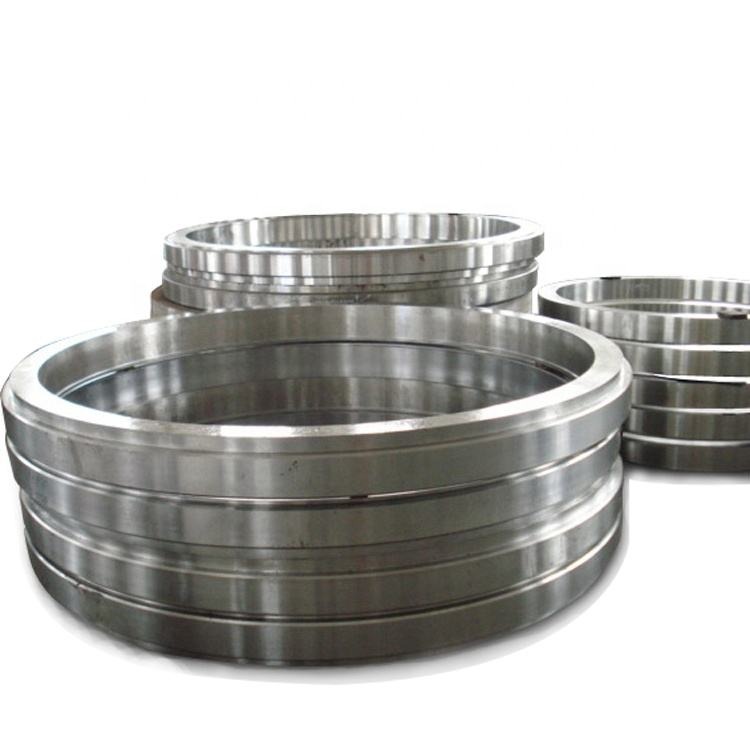

When it comes to high-performance metal components, Inconel Forgings are among the most trusted solutions for extreme environments. Whether you’re in aerospace, marine, chemical processing, or power generation, choosing the right Inconel forging can be the difference between optimal performance and catastrophic failure.
But with multiple grades, applications, and forging processes available, how do you choose the right one? This guide is here to walk you through everything you need to know — in clear, practical terms — to help you make a confident decision.
What Are Inconel Forgings?
Inconel is a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys known for their excellent resistance to heat, corrosion, and oxidation. When forged, these materials are transformed into high-strength components that can withstand intense pressures and temperatures.
Inconel Forgings refer to parts made from Inconel alloys through forging — a process that involves shaping the metal using compressive forces. Forging improves the grain structure and mechanical properties of the alloy, making it stronger and more durable than cast or machined parts.
Why Choose Inconel Forgings Over Other Materials?
Before diving into the different types of Inconel and their applications, let’s first understand why Inconel Forgings are often chosen over stainless steel, titanium, or aluminum alloys:
-
Exceptional heat resistance: Inconel retains strength even at temperatures exceeding 1000°C (1832°F).
-
High corrosion resistance: Especially in acidic, seawater, or oxidizing environments.
-
Long service life: Thanks to superior fatigue and creep resistance.
-
Great mechanical strength: Ideal for high-stress, high-pressure applications.
These qualities make Inconel a top pick for critical industries like aerospace, marine, nuclear, and chemical manufacturing.
Understanding the Forging Process
There are several methods used to produce Inconel forgings. Each has its own benefits depending on the component’s design and application.
1. Open Die Forging
Best for large parts, open die forging offers excellent strength and allows for custom shapes. Often used for shafts, rings, and large flanges.
2. Closed Die Forging
Used when precision is key, closed die forging uses shaped dies to create more complex geometries. This is ideal for high-volume parts like valves, couplings, and aerospace components.
3. Seamless Rolled Ring Forging
Ideal for creating high-strength rings used in bearings, turbines, and jet engines. This method enhances grain flow and directional strength.
Choosing the right forging method depends on size, complexity, and performance requirements.
Popular Inconel Grades and Their Applications
Not all Inconel alloys are created equal. Here’s a breakdown of the most widely used grades and where they’re typically applied.
Inconel 600
-
Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance and good oxidation resistance.
-
Applications: Used in chemical processing, food processing, and heat treating equipment.
-
Best for: General industrial use and moderate temperature environments.
Inconel 625
-
Properties: Superb strength and fatigue resistance, even at cryogenic temperatures.
-
Applications: Marine components, chemical plants, and aerospace structures.
-
Best for: High-corrosion, high-pressure settings.
Inconel 718
-
Properties: High tensile, creep, and rupture strength; excellent weldability.
-
Applications: Gas turbines, nuclear reactors, rocket motors.
-
Best for: Extreme heat and mechanical stress conditions.
Inconel X-750
-
Properties: Maintains strength at temperatures up to 700°C (1290°F).
-
Applications: Aircraft engines, nuclear reactors, and heat-treating fixtures.
-
Best for: Creep resistance in high-temperature, cyclic loading environments.
Pro Tip: Discuss your operating environment with your supplier to match the alloy to the job.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Inconel Forgings
Choosing the right forging involves more than just picking a grade. You need to evaluate several performance and design factors:
1. Operating Temperature
Always check the maximum sustained temperature the component will be exposed to. Inconel 718, for example, is more suitable for moderate to high temperatures, while Inconel 625 handles extreme corrosion environments better.
2. Corrosion Environment
Will the part be exposed to saltwater, acids, or oxidizing agents? Choose a grade like Inconel 625, which offers excellent resistance to chloride-induced corrosion.
3. Mechanical Loads
Understand the type and frequency of stress — whether tensile, compressive, or cyclic. Forgings made from Inconel 718 are ideal for components subject to high-stress fatigue cycles.
4. Component Size and Shape
Complex geometries may require closed die forging, while large, simple parts may be forged using the open die method.
5. Certification Requirements
In aerospace or nuclear applications, certifications like NADCAP, AS9100, or ISO 9001 may be mandatory. Choose a forging supplier who meets these standards.
Industries That Rely on Inconel Forgings
1. Aerospace
Inconel is a favorite for jet engine components, exhaust systems, and turbine blades due to its ability to endure high heat and pressure.
2. Marine
Saltwater environments wreak havoc on metals — but not on Inconel Forgings. Propeller shafts, valves, and marine exhaust systems are common applications.
3. Oil & Gas
From wellhead components to sealing systems, Inconel offers high strength and resistance to sour gas and hydrogen sulfide.
4. Power Generation
Used in nuclear reactors and gas turbines, Inconel stands up to thermal cycling and corrosion, making it ideal for energy systems.
5. Chemical Processing
Inconel forgings are used in reactors, heat exchangers, and pressure vessels where corrosive chemicals are processed at high temperatures.
Benefits of Custom Inconel Forgings
Sometimes, off-the-shelf parts won’t do. Custom forgings allow for:
-
Optimized design to fit exact needs.
-
Improved material utilization, reducing waste and cost.
-
Enhanced mechanical properties due to controlled grain flow.
-
Flexible production — from single pieces to large-scale batches.
Always work with an experienced forging house that can tailor your product to spec.
Inconel Forging vs. Casting: Which Is Better?
| Feature | Forging | Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Grain structure | Continuous, aligned grain | Random grain pattern |
| Strength | Higher tensile and fatigue strength | Lower overall mechanical strength |
| Porosity | Minimal to none | Possible internal porosity |
| Durability | Very high | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher upfront | Lower initial cost |
If you need strength, reliability, and precision, forging is the better choice — especially for mission-critical parts.
Choosing the Right Supplier for Inconel Forgings
Finding the right forging partner is just as important as selecting the right alloy. Here’s what to look for:
-
Experience with high-nickel alloys like Inconel
-
Certification and quality assurance processes
-
Custom forging capabilities
-
In-house testing and machining
-
On-time delivery and traceability
Don’t hesitate to request material test reports, ultrasonic inspections, and sample runs before committing.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Investing in Inconel forgings pays off in more ways than performance alone:
-
Less downtime and fewer replacements
-
Lower long-term maintenance costs
-
Reduced environmental waste due to longer component life
-
Recyclable material contributing to sustainable manufacturing
Conclusion
Choosing the right Inconel Forging starts with understanding your application’s environment, mechanical demands, and performance expectations. From aerospace to oil and gas, Inconel provides unmatched strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.






Leave a Comment